Sonography
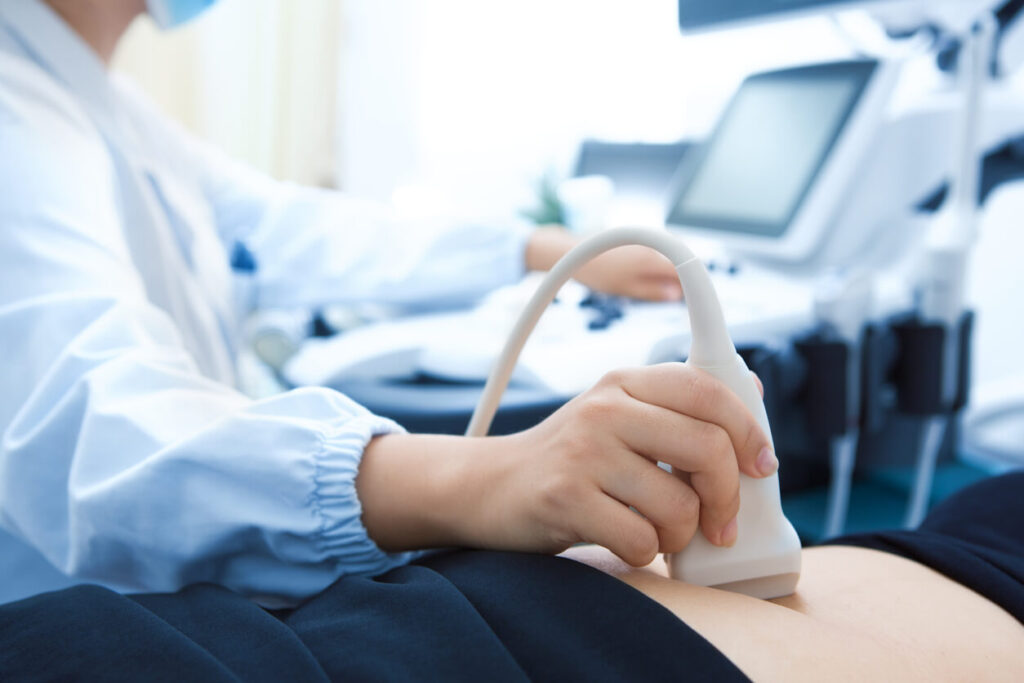
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a non-invasive medical technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal structures of the body. It is commonly used in various fields of medicine, including obstetrics, cardiology, and musculoskeletal imaging. The procedure involves placing a transducer, or ultrasound probe, on the skin over the area of interest. This device emits sound waves that bounce off tissues and organs, creating echoes that are then converted into real-time images on a monitor.
Sonography is particularly valued for its safety, as it does not involve ionizing radiation like X-rays or CT scans. It is often used to monitor fetal development during pregnancy, assess organ health, and guide biopsies or other minimally invasive procedures. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of 3D and 4D imaging, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and providing detailed views of anatomical structures.

